Hen Health
0
Hen Health
"I have written this guide to symptoms, treatments and prevention of chicken illnesses to help you when you have a sick hen. If you are still unsure what is wrong with your hen after checking this guide, please consult a vet.
As we provide this poultry health advice page free of charge, please support Durham Hens by buying health care products from us. We have everything in stock at our premises, and mail order items are sent throughout the UK with next day delivery so you get what your hens need quickly."
Margaret Manchester, Director, Durham Hens

Symptom Checker
Use this list of symptoms to find out what may be wrong with your hen, then simply scroll down the page to the green text to find an alphabetical list of problems and their treatments:
Bald Patches
- could be from mating if a cockerel is running with the hen - see Feather Pecking, Moulting, Lice, Fleas, Red Mite.
Blood in droppings
- see Coccidiosis, Worms
Chicks:
- Blood in droppings - see Coccidiosis,
- Lame - see Splayed Leg
- Huddled together - too cold (increase temperature)
- Noisy - hungry or thirsty (have food and water available at all times) or cold or hot (adjust temperature)
- Spread out at edges of brooder - too hot (reduce temperature)
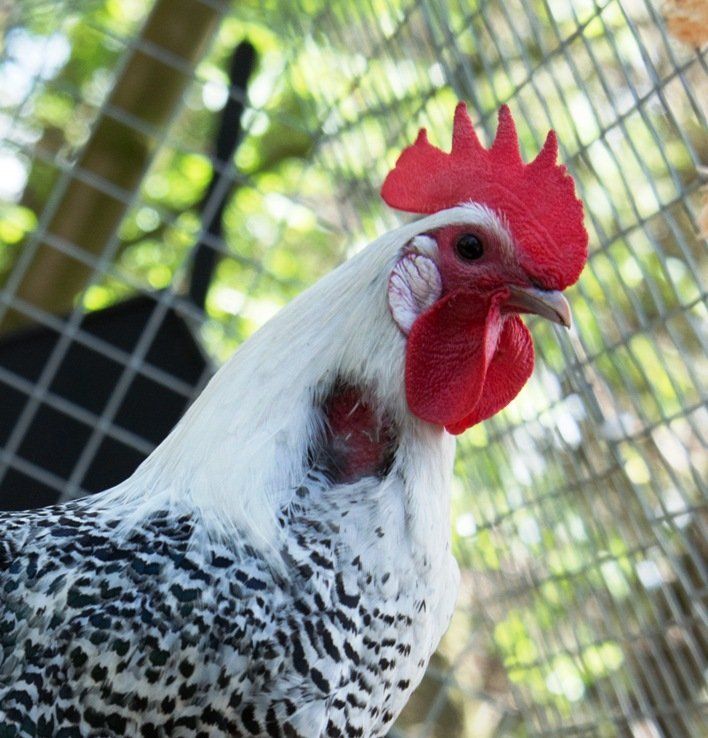
Comb:
- Orange - see Anaemia
- Pink - normal for young pullet - see Anaemia if a mature hen
- Pale - a sign of illness, look for other symptoms - see Anaemia
- Purple - not enough oxygen in the blood (Heart or Respiratory Disease)
- Black - normal skin colour for some breeds - see Frostbite, Systemic Infection
- Scabby - see Bullying, Northern Mite, Fowl Pox
- Small - normal for young pullet and some types of hen
Coughing
- could be environmental factors e.g. mould, ammonia - see Respiratory Diseases
Crop:
- Swollen and feels like a water balloon - see Sour Crop
- Hard lump in crop - see Impacted Crop
Diarrhoea
- could be too hot (hens take in more water to cool themselves down) - see Diet, Worms, Coccidiosis, Intestinal Infection
Droppings:
Normal chicken droppings vary enormously depending on what the chicken has been eating and the amount of water they have drunk. Abnormal signs in the droppings include:
- Worms - treat for worms
- Blood - see Coccidiosis
- Mucus - see Coccidiosis
- Bright green colour - Kidney Failure (but if the hen looks well, she may just have eaten lots of green food)
- Egg yolk colour - could be Egg Peritonitis
- White - see Vent Gleet
- Bad smell - see Intestinal Infection
Eggs:
- Drop in production - common in older hens, see Diet, Worms, Fleas, Red Mite, Egg Peritonitis
- Stopped laying - common in older hens, see Diet, Moulting, Egg Bound, Worms, Egg Peritonitis
- Thin shells - common in older hens, shock, see Diet, Egg Peritonitis, also give Shell Aid and Mixed Grit, add Apple Cider Vinegar or Tonic to water
- Powdery shells - extra calcium on the shell, can be caused by stress or too much calcium in the diet
- Blood spots - less common in free-range hens and those on grass, eggs OK to eat
- Watery eggs - common in older hens
- Wrinkled shells - shock, see Respiratory Diseases
Eye:
- Swollen - see Injury Eye, Sinus Infection
- Closed most of the time - a nap during the day is normal, they close their eyes if it's windy, however, if closed most of the time, this is a general sign of illness so look for other symptoms
- Bleeding - see Injury Eye, pecked by other hens, predator attack
- Missing - see a vet urgently
Face:
- Swollen - see Sinus Infection
Feathers:
- Fluffed up: a general sign of illness if the hen is hunched up, if reluctant to leave nest box see Broody
- Missing: see Feather Pecking, Moulting, Lice, Fleas, Red Mite
Gasping for air
- Shock, too hot - see Respiratory Diseases, Gapeworm
Head shaking
- Choking, Drowning - see Sinus Infection, Respiratory Diseases, Fleas, Lice, Red Mite
Legs:
- Lame - see Injury, Mareks Disease, Bumblefoot, Systemic Infection, Dehydration, Starvation
- Scaly -see Scaly Leg Mite, scales lift and dry out in old hens
Scratching
- see Fleas, Lice, Red Mite
Sneezing
- Dust, Allergy - see Sinus Infection, Respiratory Diseases
Staying out at night
- see Red Mite, Bullying
Straining
- see Egg Bound, Egg Peritonitis, Vent Injury, Constipation
Sudden Death
- see Heart Attack, Predator Attack, Injury, Poisoning
Wheezy Chest
- see Respiratory Diseases
Wings:
- Hanging Down - see Injury, Mareks disease
- Out to sides - too hot, ensure they have shade in summer
Hunched hen Friction wound
Scaly leg Fungal infection
Peck wound Feathers missing
Chicken Problems and Their Treatments
Anaemia
Symptoms: Pale comb and wattles, often caused by parasites so check the birds for mites, lice and fleas and the coop for red mite
Treatment: Poultry tonic
in drinking water, apply Red Mite Powder to the hen, clean the coop with Poultry Shield. If lethargic, give Poultry Power Drops to help to revive the chicken.
Avian Influenza
Symptoms: Swollen head, blue discolouration of neck and throat, respiratory distress, very high death rate.
Treatment: If you suspect your birds have Avian Influenza, contact a vet immediately. It is a notifiable disease.
Bird Flu
- see Avian Influenza
Broody
Symptoms: Hen sat in the nest box, feathers fluffed out, possibly aggressive behaviour, stopped producing eggs.
Treatment: All hens can go broody (which means they want to sit on eggs and hatch chicks). Some breeds are more likely to go broody, especially bantams. If you want her to hatch chicks, let her sit on fertilised eggs. See our Hatching Guide
for more information. If you don't want chicks, remove her from the nest as often as possible until she gives up. This may take up to 3 weeks and it may be advisable to wear gloves if she is aggressive. Also, block the nest box(es) off at night. If this is not successful, you could try placing her in a dog cage on grass (without the plastic base) during the day - ensure she has food and water, and also a rain cover if necessary. The cooler air outdoors should distract her from her broodiness.
Bullying
Symptoms: Feathers missing, wounds, weight loss, reluctance to leave the coop, huddled in the corner. Usually occurs soon after getting hens home or adding new hens to a flock.
Treatment: Remove from the flock if there are any open wounds, Gentian violet
to treat wounds, anti-pecking spray
to help prevent pecking, ensure the bullied hens get food and water - some hens will give up trying to eat and simply waste away! Poultry Power Drops can help to revive poorly hens. Introduce new things to the coop for distraction e.g. Vegetable Holder or hang up an old CD/DVD. Perches and screens can provide places to escape. Cockerels are very effective at controlling bullying among hens.
Bumblefoot
Symptoms: Lameness, swellings on feet, hot to touch, infection occurring after recent injury
Treatment: This requires antibiotic treatment. Clean the affected foot in antibacterial solution and take the chicken to a vet.
Coccidiosis
Symptoms: Diarrhoea sometimes with blood or mucus, most commonly found in chicks and young birds, can result in death or leave permanent damage to the gut if not treated.
Treatment: This requires Baycox treatment from a vet. Clean coop, drinkers and feeders thoroughly with Poultry Shield. Herb 'n' Thrive can be used as an organic alternative to medication.
Prevention: Vaccination with Paracox, feeding a chick crumb containing a coccidiostat, good hygiene.
Constipation
Symptoms: Straining (easily confused with egg bound which is more common)
Treatment: Clean vent area if it's dirty, provide access to water at all times, add greens to the diet and drop vegetable on to the tongue. Also, the vent can be lubricated with vegetable oil or baby oil.
Dehydration
Symptoms: Unsteady on feet, loss of balance, lethargic.
Treatment: Provide fresh clean water, if not drinking use dropper to drip water into the bird's tongue. Don't force water down the throat as she could drown. Poultry Power Drops help to revive poorly hens. Dehydration may be a symptom of another condition - look for other symptoms e.g. crop problems, bullying, etc.
Diarrhoea
Symptoms: Runny droppings, dirty feathers around vent (bottom).
Treatment: Ensure plenty of clean drinking water is available. Feed only layers pellets
or mash, with a little mixed corn
if it's winter until the problem improves. Do not give greens or kitchen scraps. If hen looks well otherwise, try Herb'n'Thrive
which effective against minor bacterial infections. Poultry Power Drops will help to revive poorly hens. A Tonic
will help the hen recover if the problem has been long-lasting. If you haven't wormed the flock recently, treat with Verm-X. If severe see Intestinal Infection.
Diet
A healthy diet is essential for the health of your hens. From about 16-20 weeks of age, they should be fed on layers pellets
or layers mash. This is a complete food designed for laying hens. There are many brands around at variable prices. Choose one from the higher end. Hens eat approximately 1kg of food per week but this will vary depending on whether or not they are free-range, and also on the temperature and time of year.
In winter hens need more calories to keep warm. If they struggle to stay warm they will not produce eggs. Feed mixed corn as well during cold spells - about one handful to two hens per day. This can be scattered on clean ground; hens enjoy pecking for grain. A small amount of greens is good for hens but if fed to excess the hens will get diarrhoea and/or lay soft-shelled eggs, or even stop laying altogether. Poultry Power Drops are a healthy treat option and help prevent boredom.
Mixed poultry grit
should be provided in a separate container. This contains calcium for making egg-shells and small flint pebbles that are needed to grind food in the hen's crop.
Clean water should be available at all times. Hens in lay will drink approximately a third of a litre each per day. Supplements such as poultry tonic
and apple cider vinegar
can be added to drinking water.
Egg Bound
Symptoms: Hen looks like she is straining with her bottom close to the ground
Treatment: Rub vegetable oil or baby oil around the vent, if the egg is broken inside the hen there is a severe risk of infection so please see a vet as soon as possible. This condition can lead to Prolapse.
Egg Peritonitis
Symptoms: Swollen abdomen, loss of weight, laying soft-shelled or no eggs at all, hen generally looks unwell, if the infection is severe there may be respiratory distress (gasping) and dark comb.
Treatment: This requires antibiotic treatment from a vet
Feather Pecking
Symptoms: Feathers missing, broken skin, flesh wound if severe, can occur when new hens are introduced to a flock, if their diet lacks protein (see Diet), or if they are over-crowded or bored!
Treatment: Gentian Violet Spray
for open wounds
Prevention: Anti-pecking spray
on new hens, spray No Fight into the coop, prevent hens from becoming bored (provide more space to forage, add perches in the run, give peck blocks
etc).
Fleas
Symptoms: Small insects that can sometimes be seen jumping, reduction in egg production, anaemia, hens scratching. Owners may be bitten around the ankles but chicken fleas cannot live on humans.
Treatment: Apply Red Mite Powder directly onto the hen, especially under the wings and around the bottom, clean the coop with Poultry Shield. Also Tonic
in water.
Prevention: Use Red Mite Powder regularly inside the coop and on your hens.
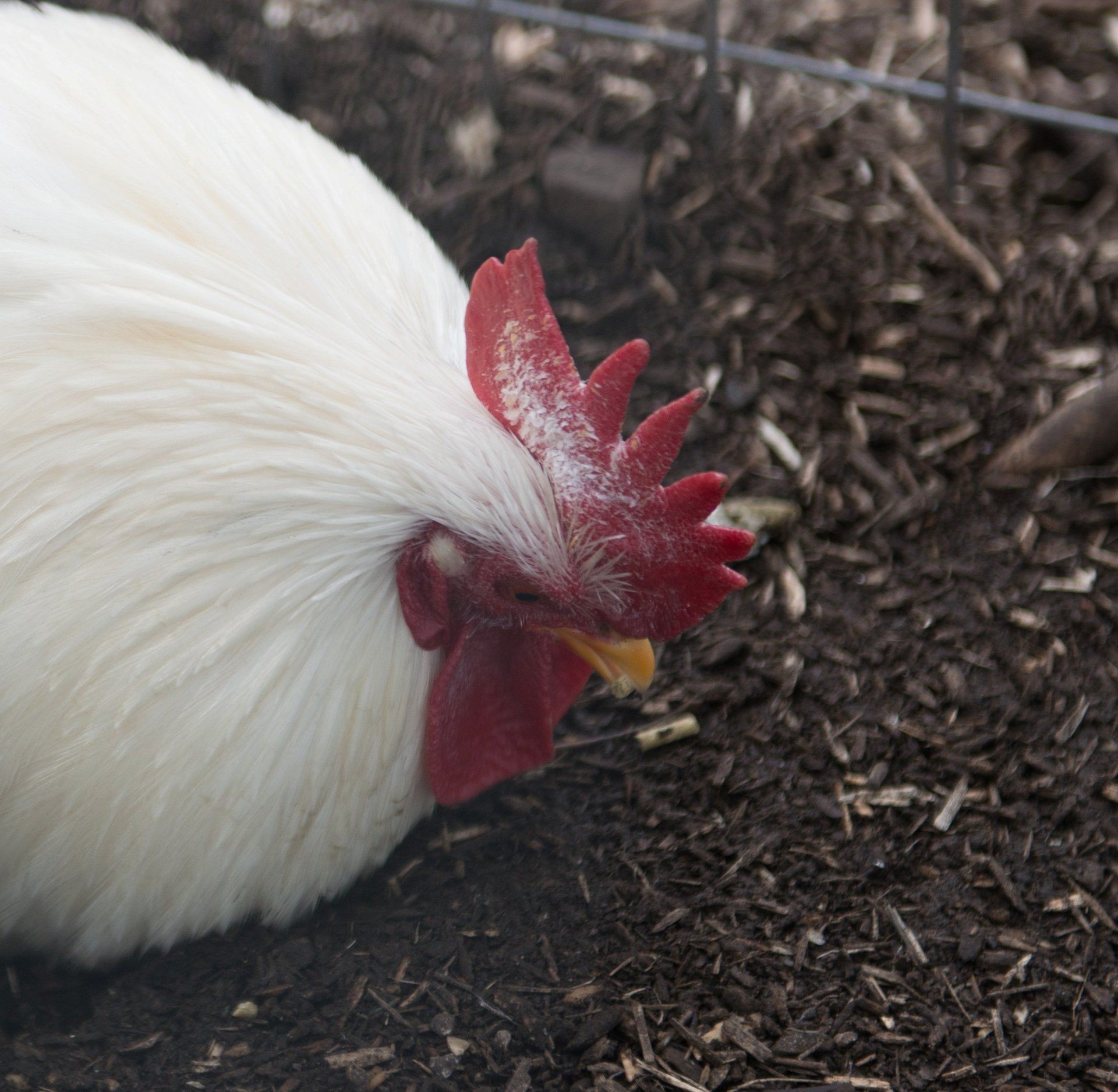
Fowl Pox
Symptoms: White blisters on comb and wattles which scab over. Scabs fall off after a few weeks. Hens in the UK are not vaccinated for Fowl Pox, but commercially reared birds in the USA are.
Treatment: Viral infection so there is no treatment available, isolate birds, most will make a full recovery, tonic
will help.
Prevention: Vaccine is available to large scale breeders. Hybrid hens are routinely vaccinated for fowl pox.
Frostbite
Symptoms: Comb turns black especially at the tips, the tips may fall off if the frostbite is severe. This can be fatal. Cockerels are more likely to be affected than hens as they do not sleep with their heads under their wing.
Prevention: Rub Vaseline on cockerel's comb during cold spells.
Gapeworm
Symptoms: Gasping, head shaking, neck stretching, gurgling sound (N.B. Symptoms very similar to Respiratory Diseases)
Treatment: This requires Flubenvet as prescribed by a vet.
Heart Attacks
Symptoms: Sudden death, usually in older or overweight chickens, can be a result of stress/fright.
Treatment: None available.
Heart Disease
Symptoms: Dark comb, listless, usually in older or overweight chickens.
Impacted Crop
Symptoms: Hard lump in the crop, watery droppings
Treatment: Drip vegetable oil or olive oil onto the hen's tongue, don't force liquids down her throat or she may drown. Once in the crop try to massage the lump so it breaks up and can be passed through the digestive system. If this does not work, see your vet. Poultry Power Drops help to revive poorly hens.
Prevention: Use wood shavings
instead of straw or hay for bedding. Don't pick long grass for them to eat. Ensure poultry grit
is available at all times.
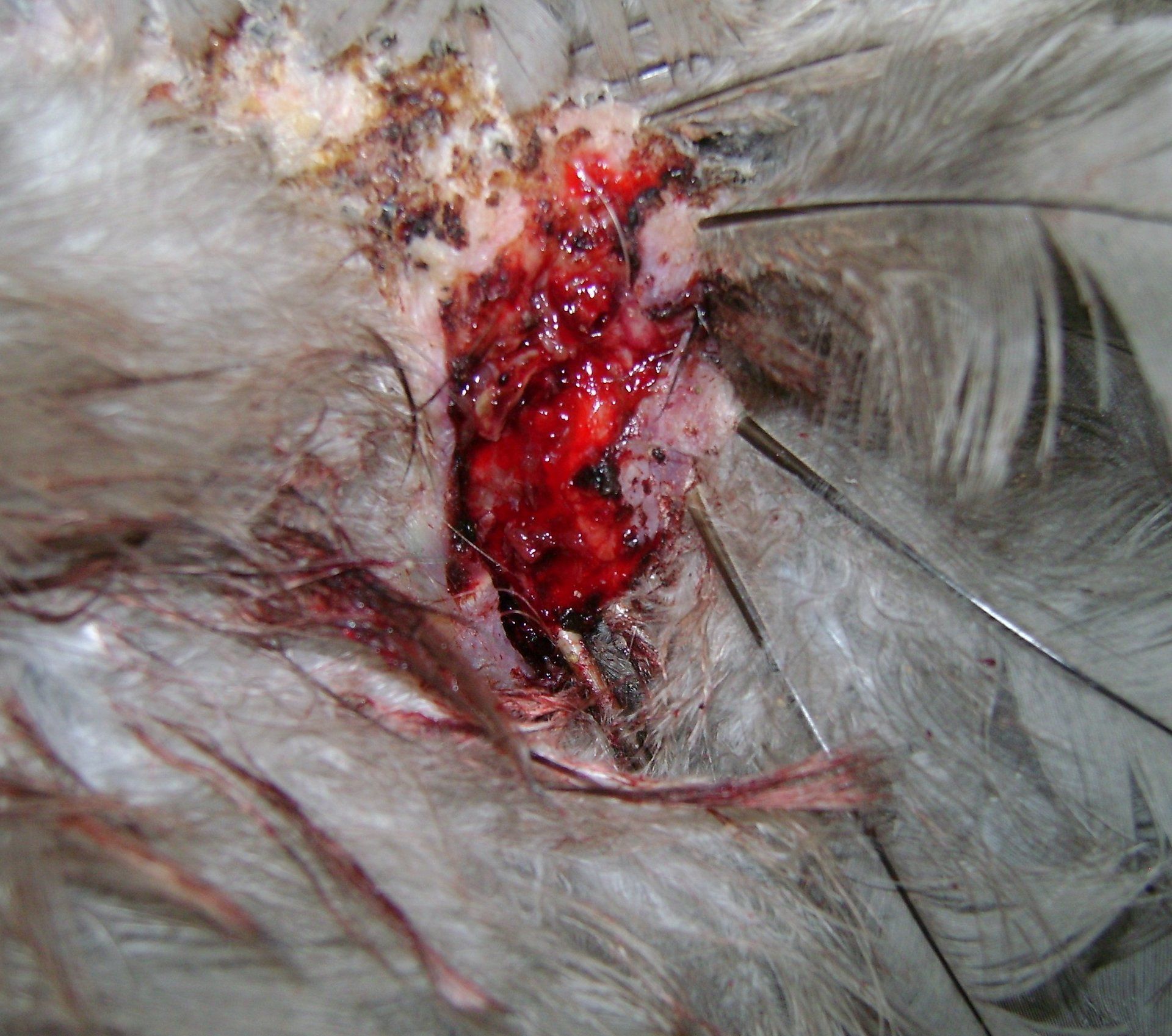
Injury:
Open wound
Symptoms: Bleeding
Treatment: If severe apply pressure to stop the bleeding, see a vet if a deep cut needs stitches, for grazes, clean the wound and apply
Gentian Violet Spray. Remove from the flock until the wound has stabbed over.
Muscle/Soft Tissue
Symptoms: Limping
Treatment: Limit the hen's movement to rest the damaged limb, make sure she can reach food and water easily. The damage should heal in time. Remove perches to prevent the hen from jumping which can worsen the injury.
Eye
Symptoms: Bleeding, swelling. Can be caused by pecking, an accident, a foreign object in the eye, sometimes the eye can be missing altogether.
Treatment: Bathe the eye area carefully to see the damage, remove the foreign object if possible, she may need anti-bacterial eye drops from your vet, if the eye is absent see your vet as soon as possible.
Vent
Symptoms: Blood around the vent, straining. Can be caused by pecking, or laying the first egg or a large egg.
Treatment: Remove from the flock, spray with Gentian Violet to prevent infection.
Intestinal Infection
Symptoms: Diarrhoea, looks generally unwell, not eating, gasping for breath if severe
Treatment: Herb'n'Thrive
is effective against minor bacterial infections. If severe consult a vet.
Prevention: To not feed out of date scraps or mouldy food to hens. Keep food and water dispensers clean, position them in the coop so other birds and wildlife are less likely to pass on bacterial and viral infections.
Lice
Symptoms: small insects (1-4mm) crawling on the hen's skin, white spots at the base of the feather are eggs, reduction in egg production, scratching. Lice feed off dead skin. They are irritating but harmless.
Treatment: Apply Red Mite Powder directly onto the hen once a week for three weeks, make sure the powder gets through the feathers and into the skin, clean the coop with Poultry Shield.
Prevention: Use Red Mite Powder inside the coop and provide a dust bath.
Marek's Disease
Symptoms: Common viral infection that causes internal tumours to grow, often resulting in paralysis of one leg and/or one wing, loss of mobility, death. Usually occurs in birds between 12 and 30 weeks old.
Treatment: None
Prevention: Vaccination at day old or as young as possible. All the hens and chicks sold by Durham Hens are vaccinated against Mareks Disease and this makes it less likely that they will suffer from this disease, although no vaccine gives complete protection.
Moulting
Symptoms: Losing feathers, not laying
Treatment: Natural process that occurs once a year usually in autumn or winter. Poultry Spice
can help hens recover more quickly.
Northern Mite
Symptoms: small insects (less than 1mm) crawling on the hens, anaemia, scratching, reduction in egg production
Treatment: Apply Smite Organic Powder or directly onto the hen, especially under the wings and around the bottom, clean the coop with Poultry Shield. Also Tonic in water.
Prevention: Use Red Mite Powder or regularly inside the coop and on your hens.
Poisoning
Symptoms: Sudden death, hens very unwell, may produce gurgling sound, bleeding from orifices (with rat poison), often strongest hens affected
Treatment: See a vet
Prevention: Do not put down rat poison, lawn fertiliser, weed killer or slug pellets where chickens can eat them.
Prolapse
Symptoms: Internal tissues sticking out of the vent, possibly bleeding if damaged or pecked by other hens, hen distressed.
Treatment: Remove the hen from the flock and take to a vet. This problem is likely to recur without surgery.
Red Mite
Symptoms: Anaemia, scratching, reluctance to go into the coop and/or lay in nest boxes
Detection: Use Red Mite Alert
to detect the presence of red mite in your coop.
Treatment: Apply Red Mite Powder
directly onto the hen, especially under the wings and around the bottom, clean the coop with Poultry Shield. Also, add Tonic to the drinking water.
Prevention: Use Red Mite Powder regularly inside the coop and on your hens.
Respiratory Diseases
(many with similar symptoms and treatments)
Symptoms: Coughing, sneezing, wheezing chest, head shaking, discharge from nostrils, possibly wrinkly eggshells.
Treatment: Separate the hen from flock, give Respite
or antibiotics from your vet. Poultry Power Drops can help to revive poorly hens.
Scaly Leg Mite
Symptoms: Scales lifted on legs
Treatment: Apply Scaly Leg Spray and then Vaseline.
Sinus Infection
Symptoms: Swollen patch below the eye on one or both sides, if severe the eye area may be swollen too, also water/pus from eye/nostril.
Treatment: Separate hen from the flock, if mild use Herb 'n' Thrive,
or if severe you will need antibiotic from a vet. Poultry Power Drops can help to revive poorly hens.
Sour Crop
Symptoms: The crop will feel soft and squishy like a water balloon.
Treatment: Tip the hen forward to allow the fluid to pour out of the crop through her mouth (CAUTION: do not hold her like this for more than a few seconds at a time as she needs to breathe!) Sour crop is caused by a fungal infection. Feed natural yoghurt. If it doesn't improve quickly, see your vet for anti-fungal treatment.
Prevention: Don't give hens grass cuttings.
Splayed Leg
Symptoms: In newly hatched chicks, one leg sticks out awkwardly, unable to walk/stand.
Treatment: Tie a piece of wool around one leg at about knee height, leave about 2cm loose between the legs and then tie to the other leg at the same height. This will act as a splint and keep the legs in the correct position. Remove after 2 days or when the chick can walk unaided.
Starvation
Symptoms: Hen will feel light, lack of energy, hunched, sitting alone.
Treatment: Remove the hen from the flock and feed separately. If reluctant to eat, give Poultry Power Drops to encourage her appetite, and add Tonic
to the drinking water.
Systemic Infection
Symptoms: Black comb, lethargy, hunched, not feeding well, sometimes lameness.
Treatment: See a vet
Vent Gleet
Symptoms: White diarrhoea
Treatment: Wash the vent area with a mild antiseptic e.g. Dettol, feed the recommended diet, without treats, and provide grit, this condition is not contagious.
Worms
Symptoms: diarrhoea, blood in droppings, loss of weight
Treatment: Worm with Flubenvet
Prevention: Give Verm-X Poultry Pellets or Verm-X Poultry Liquid
regularly to help prevent worms.
Address
Durham Hens LimitedVine HouseTow LawCounty DurhamDL13 4BNTel: 07763929686
Opening Hours
Friday 10am-4pm
Saturday 10am-4pm
Choose your hens and browse
in our shop!
Cash and electronic payments welcome.
Click & Collect
Monday 10am-4pm
Tuesday 10am-4pm
Wednesday Closed
Thursday 10am-4pm
Friday 10am-4pm
Saturday 10am-4pm
Sunday Closed
Terms and Conditions
Copyright Durham Hens Limited 2023